HuggingFace Transformers#
This tutorial demonstrates how deepchecks.vision can be used on a Hugging Face transformer model. We will use deepchecks to compare the performance of the DETR ResNet transformers model against the widely used YOLOv5s model on the COCO dataset.
Implement a DetectionData Class for the DETR Model#
In order to use the DETR model, we need to wrap the COCO DataLoader with a custom deepchecks.vision.DetectionData class, which is
a subclass of deepchecks.vision.VisionData. This class enables deepchecks to interact with your model and data and transform them to
this pre-defined format, which is set for each task type. To read more about the DetectionData class, please refer
to the Data Classes user guide.
We’ll start by loading the DETR ResNet model from the Hugging Face Transformers library:
import torch
from transformers import DetrForObjectDetection
device = torch.device("cuda") if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.device("cpu")
detr_resnet = DetrForObjectDetection.from_pretrained('facebook/detr-resnet-50')
detr_resnet = detr_resnet.to(device)
detr_resnet = detr_resnet.eval()
And then we’ll move on to implementing the COCODETRData class, subclassing the deepchecks DetectionData class. The
implementation of the infer_on_batch method is a a bit cumbersome, as it includes both the logic needed to perform
inference using the DETR model and the code needed to convert it’s outputs to the format required by deepchecks. More
on the format required by deepchecks can be found in the
following guide.
from typing import Union, List, Iterable
import numpy as np
from deepchecks.vision.detection_data import DetectionData
import torchvision.transforms as T
class COCODETRData(DetectionData):
"""Class for loading the COCO dataset meant for the DETR ResNet50 model, inherits from `deepchecks.vision.DetectionData`.
Implement the necessary methods to load the images, labels and generate model predictions in a format comprehensible
by deepchecks.
"""
# This is the list of classes returned by the DETR model. Stored in order to convert to the same class order as the
# COCO dataset used by the YOLOv5s model.
DETR_CLASSES = [
'N/A', 'person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus',
'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light', 'fire hydrant', 'N/A',
'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse',
'sheep', 'cow', 'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'N/A', 'backpack',
'umbrella', 'N/A', 'N/A', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee', 'skis',
'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove',
'skateboard', 'surfboard', 'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'N/A', 'wine glass',
'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple', 'sandwich',
'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake',
'chair', 'couch', 'potted plant', 'bed', 'N/A', 'dining table', 'N/A',
'N/A', 'toilet', 'N/A', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard',
'cell phone', 'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'N/A',
'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear', 'hair drier',
'toothbrush'
]
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
# Create a transform to pre-process the images into a format acceptable by the DETR model.
self.transforms = T.Compose([
T.Resize(800),
T.ToTensor(),
T.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
# Build a dict translating the classes DETR was trained on to the classes YOLO was trained on.
# DETR classes, listed in DETR_CLASSES, include 'N/A' classes which didn't exist in the YOLO version of COCO
# data.
self.label_translation = {}
detr_shift = 0
for i in range(len(self.DETR_CLASSES)):
if self.DETR_CLASSES[i] == 'N/A':
detr_shift += 1
self.label_translation[i] = i - detr_shift
def batch_to_labels(self, batch) -> Union[List[torch.Tensor], torch.Tensor]:
"""Convert the batch to a list of labels. Copied from deepchecks.vision.datasets.detection.coco"""
def move_class(tensor):
return torch.index_select(tensor, 1, torch.LongTensor([4, 0, 1, 2, 3]).to(tensor.device)) \
if len(tensor) > 0 else tensor
return [move_class(tensor) for tensor in batch[1]]
def batch_to_images(self, batch) -> Iterable[np.ndarray]:
"""Convert the batch to a list of images. Copied from deepchecks.vision.datasets.detection.coco"""
return [np.array(x) for x in batch[0]]
def _detect(self, im, model, device):
"""A helper function. Applies DETR detection to a single PIL image."""
def box_cxcywh_to_xyxy(x):
"""Convert bounding box format from [cx, cy, w, h] to [xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax], when c is "center"."""
x_c, y_c, w, h = x.unbind(1)
b = [(x_c - 0.5 * w), (y_c - 0.5 * h),
(x_c + 0.5 * w), (y_c + 0.5 * h)]
return torch.stack(b, dim=1).clip(0, 1)
def rescale_bboxes(out_bbox, size):
"""Rescale bounding boxes from the DETR model's normalized output to the original image size."""
img_w, img_h = size
b = box_cxcywh_to_xyxy(out_bbox)
b = b * torch.tensor([img_w, img_h, img_w, img_h], dtype=torch.float32)
return b
# Apply the transform to the image.
img = self.transforms(im).unsqueeze(0)
# propagate through the model
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(img.to(device))
# keep only predictions with 0.7+ confidence
probas = outputs['logits'].softmax(-1)[0, :, :-1].cpu()
keep = probas.max(-1).values > 0.7
# convert boxes from [0; 1] normalized units to image scales.
bboxes_scaled = rescale_bboxes(outputs['pred_boxes'][0, keep].cpu(), im.size)
return probas[keep], bboxes_scaled
def _convert_to_80_labels(self, labels):
"""Use the pre-built self.label_translation to translate the DETR predictions to YOLO COCO classes."""
return torch.Tensor([self.label_translation[label] for label in labels]).reshape((-1, 1))
def infer_on_batch(self, batch, model, device) -> Union[List[torch.Tensor], torch.Tensor]:
"""Infer on a batch of images and return it in deepchecks format.
Return a list of prediction tensors (one for each image) containing in each row:
[x_min, y_min, width, height, confidence, class_id]
"""
processed_preds = []
# Iterate over images in the batch
for batch_idx in range(len(batch[0])):
probas, bboxes_scaled = self._detect(batch[0][batch_idx], model, device)
bboxes_scaled[:, 2:] = bboxes_scaled[:, 2:] - bboxes_scaled[:, :2] # xyxy to xywh
if len(probas) > 0:
processed_pred = torch.cat([bboxes_scaled, # xywh bbox coordinates
probas.max(dim=1)[0].reshape((-1, 1)), # confidence
self._convert_to_80_labels(probas.argmax(dim=1).tolist())],
# translated class id
dim=1)
processed_preds.append(processed_pred)
return processed_preds
We can now create COCODETRData objects for the training and test data, and run the validation described here to make sure our class is working as expected:
from deepchecks.vision.datasets.detection import coco
detr_train_ds = coco.load_dataset(batch_size=8)
detr_test_ds = coco.load_dataset(batch_size=8, train=False)
detr_train_ds.validate_format(detr_resnet, device)

Great! We can see that the labels match the object locations, and that the labels an detections align.
Load COCO and YOLOv5s#
Next, we’ll load from deepchecks.vision.datasets.detection.coco a sample of the COCO dataset (coco 128) and
the YOLO model, both downloaded from ultralytics repository. We’ll use yolo
to benchmark the results achieved by the DETR model.
yolo_train_ds = coco.load_dataset(object_type='VisionData')
yolo_test_ds = coco.load_dataset(object_type='VisionData', train=False)
yolo = coco.load_model()
We already loaded the data wrapped with the relevant VisionData object, so we can just use the
MeanAveragePrecisionReport check to
evaluate the model’s performance for various IoU thresholds and bounding box sizes.
from deepchecks.vision.checks import MeanAveragePrecisionReport
yolo_map_result = MeanAveragePrecisionReport().run(yolo_test_ds, yolo, device=device)
yolo_map_result.show()
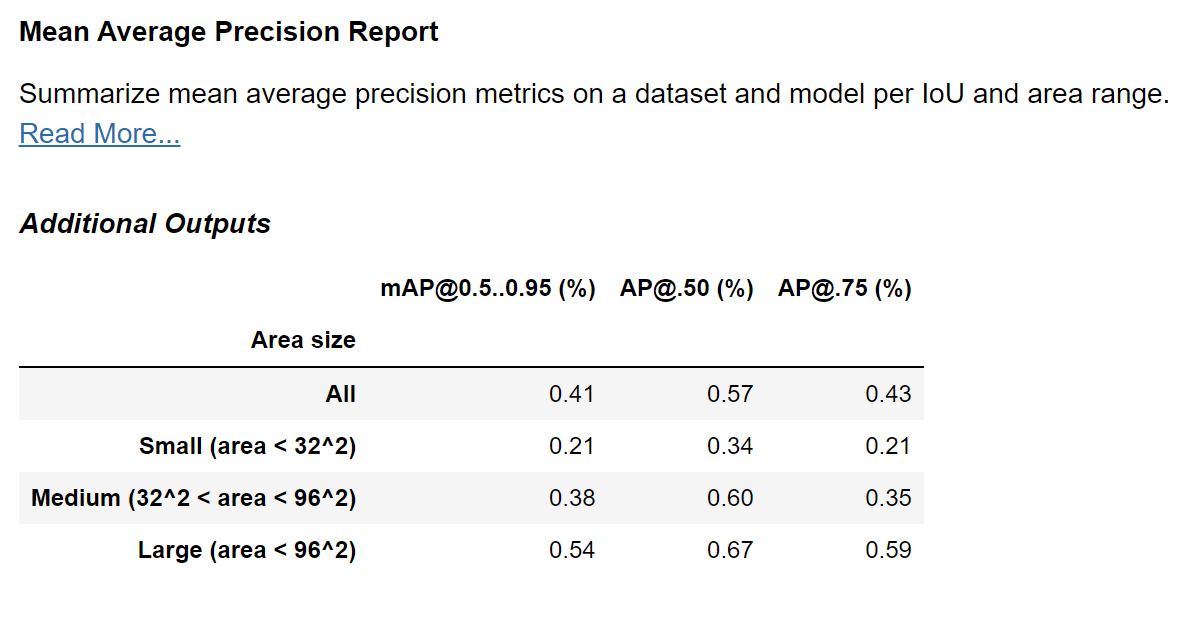
Benchmarking YOLOv5s Against DETR ResNet#
Now that we have everything in place, we can run the MeanAveragePrecisionReport check also on the DETR model! Let’s run and compare to the YOLO results.
# The test data contains the same dataloader as the yolo_test_ds, the only difference being them being wrapped by
# different subclasses of DetectionData facilitating the interface to the different models.
detr_map_result = MeanAveragePrecisionReport().run(detr_test_ds, detr_resnet, device)
detr_map_result.show()
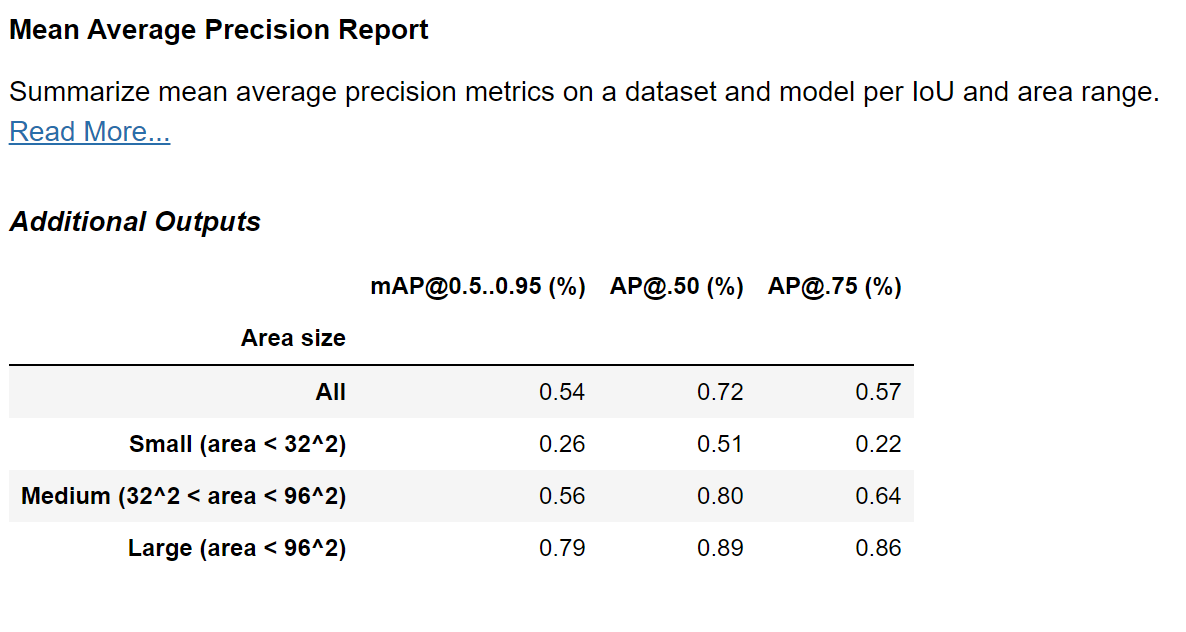
Comparing to the results achieved earlier with YOLO:
yolo_map_result.show()

We can clearly see an improvement in the DETR model! We can further see that the greatest improvement has been achieved for the larger objects, with objects of sizes of up to 32^2 squared pixels improving only from an mAP of 0.21 to 0.26.
Of course, now that the DETR interface class (our COCODETRData) has been implemented we can go on and run any deepchecks check or suite. You can check them out in our check gallery, and learn more about when you should use each of our built-in suites.